The probable date of delivery is the estimated term to give birth, calculated from the last menstruation and / or the development of the fetus. A pregnancy comes to an end at 38 weeks, and although 40 weeks are estimated to give that probable date, it is considered normal for the pregnancy to reach 42 weeks.
About 10% of deliveries occur at 42 weeks. The most common cause of prolonged or post-term pregnancies is that the due date was miscalculated and in fact is in previous weeks. But if they exceed 42 weeks of pregnancy there are certain risks to the health of the mother and the baby.
Risks for the baby after week 42 of pregnancy
As the pregnancy passes from the probable date of delivery, the placenta, which is the organ that forms inside the uterus during pregnancy and helps to nourish the baby and filter excess waste, can stop working as effectively as I did it before. And it is that the placenta is maturing throughout pregnancy, becoming considered old placenta or hypermadura.
This could influence the amount of oxygen and nutrients the baby receives, so the function of nourishing and protecting the baby can be compromised. Before him risk that the placenta is no longer fulfilling its functions well, the delivery is delayed and the baby does not feed as one would expect doctors may consider inducing labor.
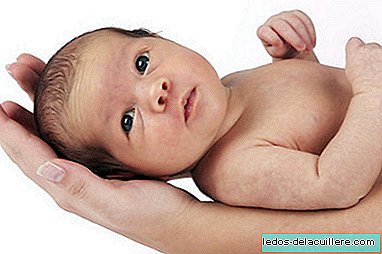
The syndrome of immaturity (or post-maturity) refers to babies with characteristics of placental insufficiency: the baby has nails and long hair, a long and thin body and wrinkled or parchment-like skin.
Also, as the baby continues to grow, the amount of surrounding amniotic fluid may decrease. When this happens, the umbilical cord can be compressed with the baby's movements or uterine contractions. This can also interfere with the baby's ability to receive appropriate amounts of nutrients and oxygen.
 In Babies and more Induction of labor: in which cases it is performed, when and what risks it entails
In Babies and more Induction of labor: in which cases it is performed, when and what risks it entails Aspiration of the meconium, the first feces of the baby: the baby can defecate in a smaller amount of amniotic fluid and then inhale it into the lungs, what is known as meconium aspiration syndrome. This can cause a inflammation in the baby's lungs, although frequently it is only born with meconium spots and the severity of aspiration is not much.
Macrosomia occurs when the baby grows too much and this makes it difficult to be born through the vaginal canal, although it is usually cases of diabetes of the mother and not the growth of the last weeks that causes it.
Fetal death It occurs when the baby dies in the womb. It is a rare event in which various factors usually converge, but the risk increases in the weeks after the probable date of delivery.

Risks to the mother
For the mother, exceeding 42 weeks of pregnancy leads to higher rates of perineal lesions, since babies born after the probable date of birth tend to be older and this causes more trauma to the mother's back during childbirth.
There are also higher rates of caesarean section: fetal distress is more common during labor in the weeks after the probable date of delivery and this seems to increase the risk of a caesarean section.
Caution, but without hurry
In any case, good prenatal control especially and more often in the last weeks of pregnancy it will help to detect the majority of problems, such as heartbeat, fetal activity and the presence of amniotic fluid, and many times it is when the baby is ready the moment the baby starts childbirth process, near the dreaded 42 weeks of gestation.
 In Babies and more, what risks exist if delivery is delayed?
In Babies and more, what risks exist if delivery is delayed?Although many doctors already take the 41st week as an indicator to schedule a delivery, without apparent problems and in fact the baby does not "delay", because of the risk that the probable date was poorly calculated.
While is true that there are real risks when exceeding 42 weeks of pregnancy, the majority of babies of prolonged pregnancies are born healthy, and to advance a childbirth without reason even at week 40 would seem to go against nature and not let it act, assuming new risks.